How We Treat
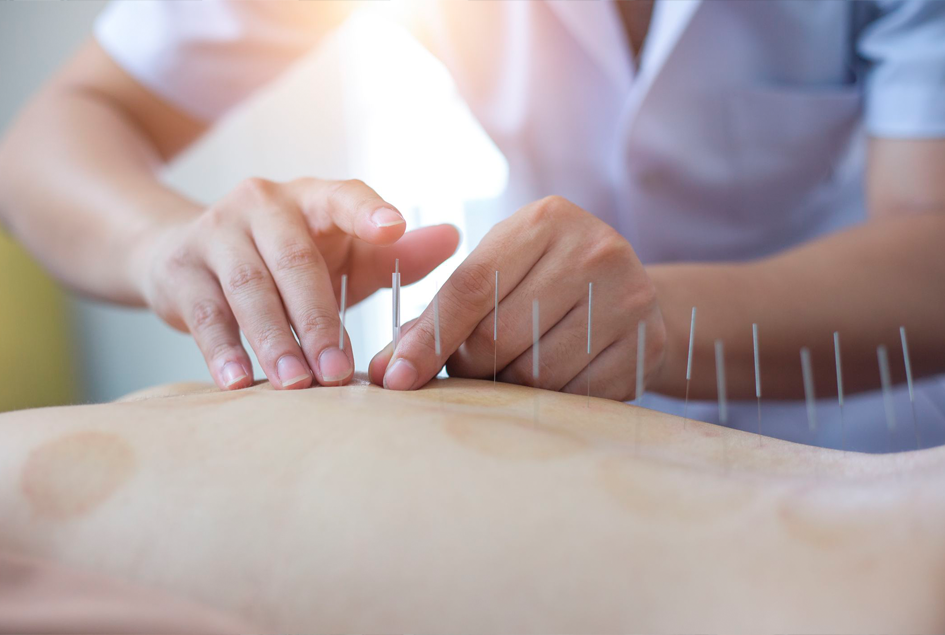
Acupuncture
Western medical acupuncture is the use of acupuncture following a medical diagnosis , using scientific studies and evidence based practice. It involves stimulating sensory nerves under the skin and in the muscles using needles.
This results in the body producing natural substances, such as pain-relieving endorphins and enkephalins’. When the needle is inserted into a muscle, the muscle unit releases a enzyme called Acetylcholine esterase which allows the muscle unit to relax. It’s likely that these naturally released substances are responsible for the beneficial effects experienced with acupuncture. Acupuncture has been scientifically shown to stimulate the higher centres of the brain , helping the brain adapt and modulate pain.
A course of acupuncture usually creates longer lasting pain relief than a single treatment.
Maitlands
What makes the Maitland Concept special is the combination of the individual and specific treatment of the patient (both initial and ongoing) with the therapist’s clinical experience and the latest scientific findings. In addition to joint mobilisation, soft tissue and fascial mobilisation and manipulation of the extremities and spine, the approach makes use of neurodynamic techniques ( movement of the nervous system), muscle stretching, strengthening and stabilising exercises specifically adapted to the individuals requirements.
McKenzie
The McKenzie method exists of 3 steps: evaluation, treatment and prevention. The evaluation is received using repeated movements and sustained positions. With the aim to elicit a pattern of pain responses, called centralisation, the symptoms of the lower limbs and lower back are classified into 3 subgroups: derangement syndrome, dysfunction syndrome and postural syndrome. The aims of the therapy are: reducing pain, centralization of symptoms (symptoms migrating into the middle line of the body) and the complete recovery of pain. All exercises for the lumbar spine are repeated a number of times to end-range on spinal symptoms in one direction. When you do only 1 repetition, this will cause pain. When you repeat it several times the pain will decrease. Also after movement termination the changes in pain intensity can persist, which leads to a treatment modality.
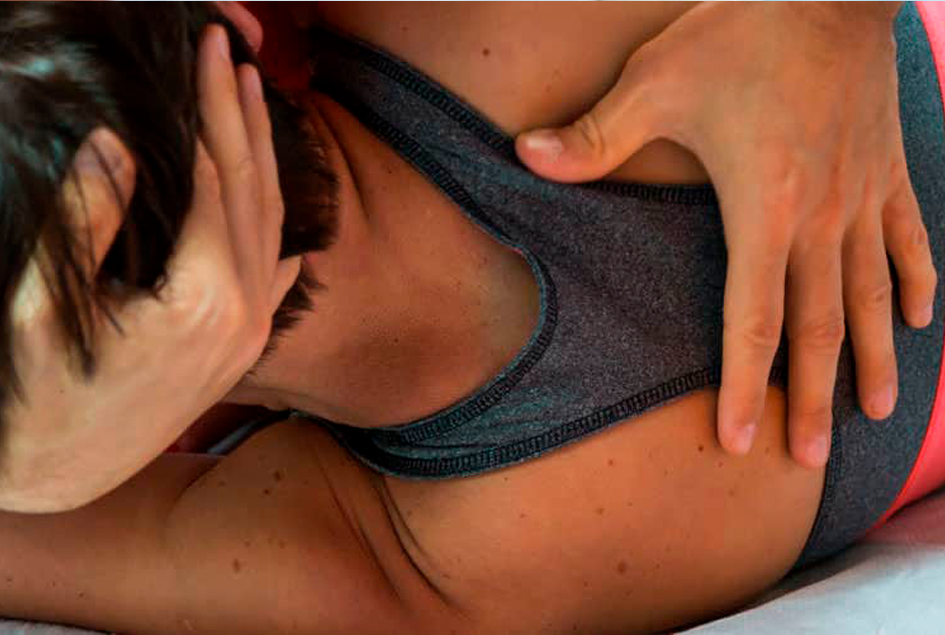

Mulligan
Mulligan Manual Therapy can be used to help treat a variety of injuries and pain including neck pain, back pain and upper and lower extremity injuries. Designed to reduce pain and improve the patient’s range of motion the Mulligan technique involves Natural Apophyseal Glides (NAGS), Sustained Natural Apophyseal Glides (SNAGS) and Mobilization with Movement (MWM) for the treatment of musculoskeletal injuries.
When applying manual therapy techniques, a physiotherapist will identify one or more comparable signs that may include loss of joint movement, pain associated with movement or pain associated with specific functional activities. Then a passive accessory joint mobilization is applied to the joint plane and the accessory glide is to be pain free. Using various combinations of parallel or perpendicular glides, the therapist will try to find the correct treatment plane and grade of movement. When done, the comparable sign should be significantly improved by either an increase in the range of motion or absence of pain.
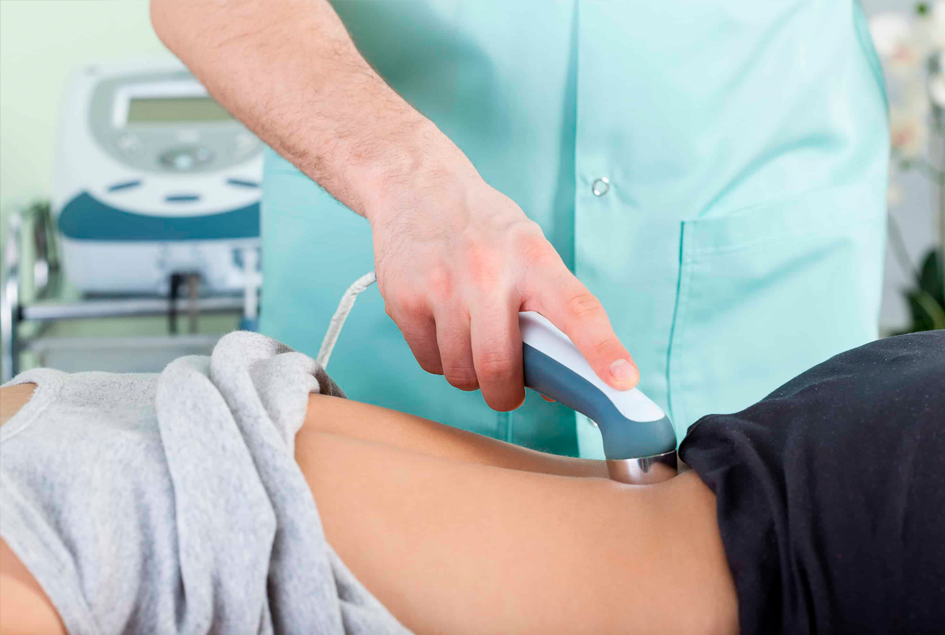
Electrotherapy
A powerful tool used by many physiotherapists, electrotherapy treats chronic pain, musculoskeletal injuries, muscle wasting, and nerve pain by using targeted and controlled electrical stimulation.
Electrotherapy is a gentle and non-invasive modality that works by stimulating nerves and muscles through the surface of the skin. Though it varies based on which device your practitioner uses, electrotherapy is thought to work in a variety of ways:
• Send out electrical impulses that block or interfere with the body’s pain signals, leading to reduced pain.
• Help release endorphins (chemical messengers) that naturally decrease pain in the body.
• Stimulate muscle tissue to contract to reduce atrophy.
• Create a heating effect within the body which improves circulation and stimulates healing.
• Stimulate cells which reduce inflammation, promote collagen production, and inhibit pain.

Exercise Therapy
Exercise therapy is defined as a regimen or plan of physical activities designed and prescribed to facilitate the patients to recover from diseases and any conditions, which disturb their movement and activity of daily life or maintain a state of well‐being through neuro re‐education, gait training, and therapeutic activities. It is systemic execution of planned physical movements, postures, or activities intended to enable the patients to reduce risk, enhance function, remediate or prevent impairment, optimise overall health, and improve fitness and well‐being.